Isometric projection:
In case of isometric projection that is the most commonly utilized axonometric projection, the view plane normal makes equal angles with the principal axes that lead to the equal foreshortening of all of the three major axes. This condition may be satisfied only if the view plane normal n in x, y and z directions are equal, that means
| nx | = | ny | = | nz |
Figure illustrated an isometric projection of a cube. In this case, all of the lines are scaled equally along with each axis. It is useful as lines which are parallel or are along the principal axes may be measured and converted easily by using the same scale.
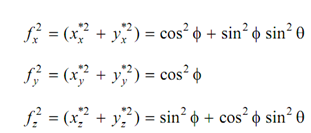
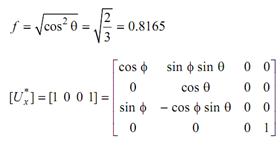
cos2 φ + sin 2 φ sin 2 θ = cos2 θ
sin 2 φ= sin 2 θ / (1 - sin 2 θ)
cos2 φ = sin 2 φ + cos2 φ sin 2 θ
sin2 φ= 1 - 2 sin 2 θ / (1 - sin 2 θ)
sin 2 θ = 1 /3
= [cos φ sin φ sin θ 0 1]
α= tan -1 (± sin 25.26439o ) = ± 30o
sin φ = cos φ for φ = 45
sin 2 φ= (1/ 3 ) / (1-(1/3)) = (½) (φ= ± 45)
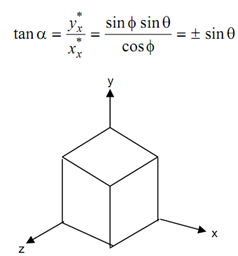
Figure: Isometric Projection