Procedure for calculation:
Rf value: It is a characteristic parameter called retardation factor and abbreviated as Rf. That represents the position of an ion or a substance along with respect to solvent phase. Rf of a solute is defined as the ratio of the rate of movement of the solute to the rate of movement of the solvent. Rf is most generally used within paper and thin layer chromatography and is considered as a characteristic of nature of the solute sample which may, of course, change with the solvent phase. It describes relative migration of the solute with respect to the solvent and may be represented as
Rf = Distance traveled by the solute/Distance traveled by the solvent
= d s/d m
Where, ds and dm are linear distances measured from the line of origin whereas spots are put as describes in Figure. By definition, Rf value cannot exceed 1.0. Ideally, Rf values must be in the range of 0.1 to 0.9 with a minimum separation of 0.05. In order to have better separation, two spots have to not overlap along with each other and these must be symmetric without any tailing. In sequence to prevent tailing, different solvent mixtures, mixed in proper ratio, must be tried. If a spot of the solute is not symmetric, then ds are measured from the position of maximum intensity or the centre of the spot.
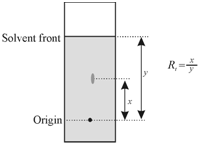
Figure: Procedure for calculation of Rf value in paper chromatography