Adsorption Chromatography:
In majority of the cases of adsorption chromatography, silica column packings are used where main mechanism is the interaction of its OH groups with the polar or unsaturated functional groups of a solute/solvent molecule by hydrogen bonding or dipole interaction. The slightly acidic silanol (Si-OH) groups in silica gel are at the surface and extend out from the surface in the internal channels of the pore structure. A number and topographical arrangement of the various kinds of OH groups, as display in Figure, determine the activity of the adsorbent and thereby the retention of the solutes. These OH groups can be divided into three types:
- silanol (free OH),
- siloxane bond (Si-O-Si) and
- hydrogen bond (Si-OH...O).
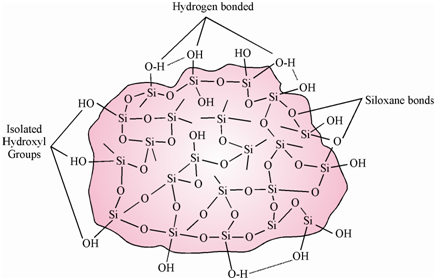
Figure: Structure of silica gel depicting the various types of hydroxyl groups that interact with the functional groups of solute/solvent molecules