Reduction of an aromatic ketone:
The resistance of the aromatic ring to reduction is helpful because it is feasible to reduce functional groups that might be attached to the ring without reducing the aromatic ring itself. For instance, the carbonyl group of an aromatic ketone can be decreased with hydrogen over a palladium catalyst without influencing the aromatic ring. This permits the synthesis of primary alkylbenzenes that cannot be synthesized directly through the Friedel-Crafts alkylation. The significance of it is noting that the aromatic ring makes the ketone group more reactive to reduction than would generally be the case. Aliphatic ketones would not be reduced within these types of conditions. Nitro groups can as well be reduced to amino groups within these conditions without affecting the aromatic ring.
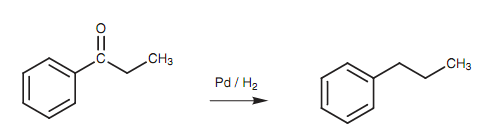
Figure: Reduction of an aromatic ketone.