Reduction:
Aromatic rings may be hydrogenated to cycloalkanes, but the reduction has to be performed under strong conditions by using a nickel catalyst, high temperature and high pressure - much stronger conditions than would be needed for the reduction of alkenes. This is due to the inherent stability of aromatic rings. The reduction can also be performed by using hydrogen and a platinum catalyst with in high pressure, or with hydrogen and a rhodium or carbon catalyst. The latter is a more powerful catalyst and the reaction can be complete at room temperature and at atmospheric pressure.
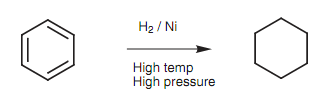
Figure: Reduction of benzene to cyclohexane.