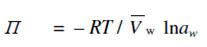Binary aqueous salt solution system:
In a binary aqueous salt solution system, let component, i represent water denoted through subscript w and let μi = μ* (chemical potential of water at a specified pressure and temperature). According to Eq., a chemical potential of water μ w in the solution at pressure P1 is less than that of pure water. *
μw = μ*w+ RT ln aw
where, aw is the thermodynamic activity of water in solution. The equilibrium could be restored through increasing the pressure on the solution side to P2 such in which the chemical potential of water is raised to that of pure water, μw. The increase in chemical potential of water in the solution as the pressure is increased from P1 to P2 is acquired from Eq.
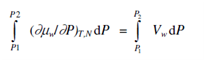
Since this increase, added to μw must restore the chemical potential of water and according to Eq.
μw +∫P2P1Vwd∫ P =μ*w
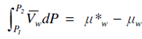
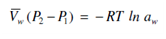
when Vw is assumed constant.
The pressure difference (P2 -P1) is through definition the osmotic pressure of the solution, usually represented through Π. Thus,
Vw Π = - RT ln aw