Peripheral Nerves
All peripheral nerves have a general basic structure. The nerve fiber consists of an axon altogether with accompanying Schwann cells. Numerous unmyelinated axons are invested by a single glial cell. Separate nerve fibers supported by connective tissue, the endoneurium, are collected into fasciculi, bundles, surrounded by a connective tissue sheath, the perineurium. The nerve may be one or numerous fasciculi all encapsulated by a connective tissue epineurium.
The two systems for the categorization of PNS nerve axons are in general use. They depend on axon diameter and conduction velocity and are summarize in next table as shown. The Erlanger and Gasser system is used to categorize both afferents and efferents. The Lloyd and Hunt scheme is used completely to define the afferent axons.
Table: Peripheral nerves
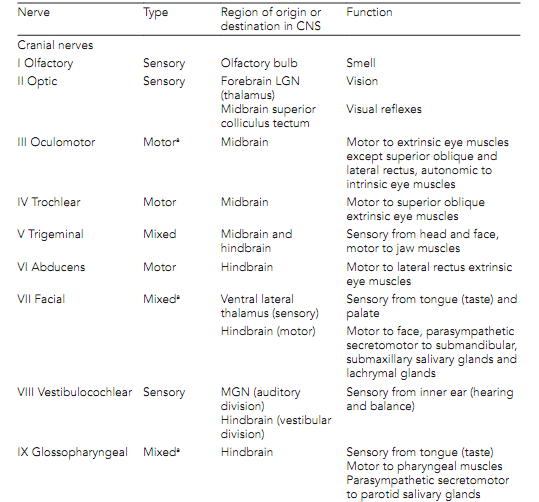
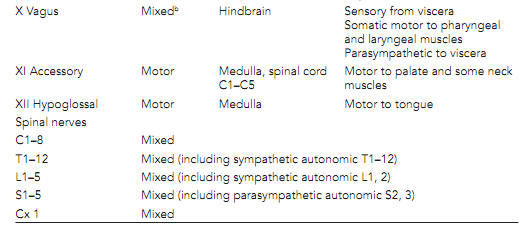
Table:Classification of peripheral nerve fibers