Polar functional groups:
It is probable to recognize the nucleophilic and electrophilic centers in common functional groups, based upon the relative electronegativities of the atoms that are present.
The subsequent guidelines are important:
1. C-C and C-H bonds are covalent. Hence, neither carbon nor hydrogen is a nucleophilic or electrophilic center;
2. Nitrogen is instantly to the right of carbon within the periodic table. The nitrogen is more electronegative however the variation in electronegativity among these two atoms is small and thus the N-C bond is not specifically polar. Hence, the carbon atom can generally be ignored like an electrophilic center;
3. O-H and N-H bonds are polar covalent. Hydrogen is a weak electrophilic center whereas Nitrogen and oxygen are very strong nucleophilic centers.
4. C=O, C=N and C≡N these three bonds are polar covalent. In this the O and N are nucleophilic centers and the carbon is an electrophilic center;
5. C-O and C-X bonds (X = halogen) are polar covalent. The oxygen atom is moderately nucleophilic while the halogen atom is weakly nucleophilic. The carbon atom is an electrophilic center.
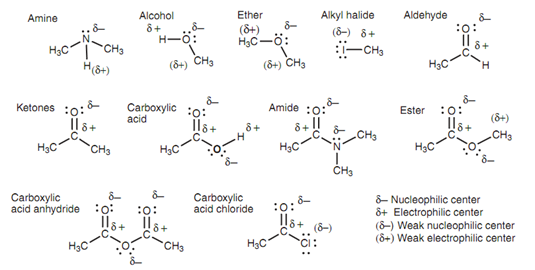
Figure: Nucleophilic and electrophilic centers of common functional groups.