Alkanes:
Alkanes are saturated compounds that have single bonds among carbon atoms and hold the maximum number of hydrogen atoms probable. Every carbon is flanked through four covalent bonds and every hydrogen atom shares one pair of electrons along with a carbon atom, as described in below figure.
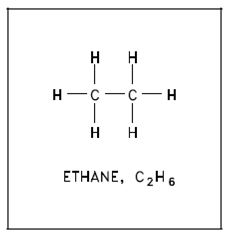
Figure: Alkane
CH4 + Br2 →CH3Br + HBr
Thermal decomposition or cracking is the procedure of breaking huge molecules within smaller ones. By using heat as a catalyst, propane could be broken within ethylene and methane:
CH4 (gas) + 2O2 (gas) → CO2 (gas) 2H2O (liquid) + 213kcal (heat)
Combustion occurs while an alkane is burned, a products being carbon dioxide gas, water and heat. Those reactions are widely exothermic and as like the hydrocarbons are often used for fuel.
C3H8 → CH4 +C2H4
Heat