Dispersion:
The index of refraction for a specific substance based on the wavelength of the light passing via it. The glass slows down the light mainly at the shortest wavelengths (blue & violet) and the least at the longest wavelengths (red &orange). This difference of the refractive index with wavelength is termed as dispersion. It is the main principle by which a prism works (figure is as shown below).The more the light is slowed down by the glass, the more its path is deflected whenever it passes via the prism. This is why prisms cast rainbows whenever white light is shone via them.
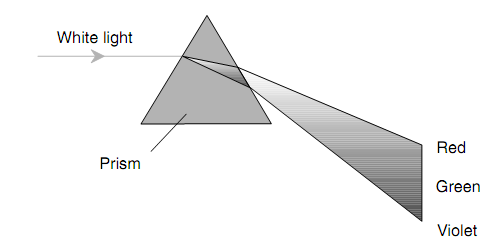
Figure: Dispersion is responsible for the fact that a glass prism "splits" white light into its constituent colors.
The Dispersion is significant in optics for two reasons. At first, a prism can be used to make a spectrometer that is a device for inspecting the intensity of visible light at particular wavelengths. (Excellent gratings are used for this). Secondly, dispersion degrades the quality of white-light images sight via simple lenses.