Olfactory bulb
The axons of ORNs run in the olfactory nerve to build excitatory synapses on the dendrites of mitral cells or tufted cells (M/T) and short axon inhibitory periglomerular cells in the olfactory bulb. M/T cells send their axons into olfactory tract. Synapses among ORNs and M/T and periglomerular cells are originated in olfactory glomeruli, spherical zone a few 150 µm across. The olfactory bulb contains around 2000 glomeruli, each receiving the terminals of 25 000 ORNs which respond to similar odors. Therefore, glomeruli are odor-specific functional units as shown in figure below. Low concentrations of a given odor molecule activate cells in the single glomerulus that gets input from the ORNs bearing odorant receptors with the maximum affinity for the molecule. At high concentrations, cells in other glomeruli are activated as their ORN odorant receptors low-affinity binding sites for the molecule are engaged. Each glomerulus has dendrites from around 75 M/T cells. The M/T cells integrate fragile inputs from a large number of ORNs in a glomerulus to produce a strong signal.
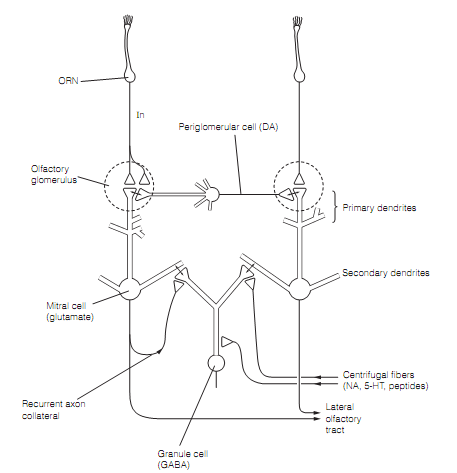
Figure: Circuitry of the olfactory bulb. Reciprocal synapses are represented by ´. Neurotransmitters used by particular cell types are shown in parentheses: Here, DA=dopamine; GABA=g-aminobutyric acid; 5-HT=serotonin; NA=noradrenaline (norepinephrine).
The lateral inhibition dampens responses from glomeruli with slightly distinct odor specificities therefore as to heighten odor discrimination. This is brought around by reciprocal dendrodendritic synapses among M/T cells and inhibitory interneurons termed granule cells. Through these synapses, M/T cells excite granule cells that then inhibit the similar, and adjoining, M/T cells.
There is a topographical organization to the fibers of the olfactory nerve and their projections to the olfactory bulb. Very thin strips of olfactory epithelium running in an anteroposterior direction go to neighboring glomeruli. A given odor excites a specificarray of glomeruli across the olfactory bulbs, an odor image. The maximum the concentration of the odor molecule the bigger the region activated.