Ohm Meter:
The ohm meter is an instrument that is used to determine resistance. A simple ohm meter that was display in below figure consists of a battery and a meter movement calibrated inside ohms and a variable resistor.
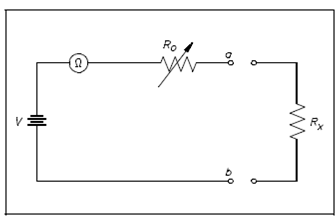
Figure: Simple Ohm Meter Circuit
Ohm meters are linked to a component that is removed from the circuit as described in Figure. The reason for removing the component is which measurement of current by the component determines the resistance. The current will flow in the path of least resistance and provide an erroneous reading if the component remains in the circuit and a parallel path exists in the circuit.
Ro, in Figure, is an adjustable resistor whose aim is to zero the ohm meter and correct for battery aging. It is also a current-limiting resistor that involves the meter resistance Rm.
Zeroing it is accomplished by shorting the ohm meter terminals ab and adjusting Ro to provide full-scale deflection.
Given Equation (14-10) is the mathematical representation for determining full-scale deflection meter current
Im = V/Ro (14-10)
While the unknown resistance Rx is linked across the ohm meter terminals, the current is measured through calculating the total series resistance and applying the Equation (14-10). Given Equation (14-11) is the mathematical representation of this concept.
I = V/Ro + Rx (14-11)
A simple way to determine ohm meter deflection is through use of a deflection factor (D). A Deflection factor is the ratio of circuit current to meter current. Given Equation (14-12) is the mathematical representation of the deflection factor.
D= I/Im =(V/Ro +Rx)/(V/Ro) = Ro/(Ro +Rx) (14-12)
The current through the circuit can be determined by solving for I. Equation (14-13) is the mathematical representation of this relationship.
I = D Im (14-13)
To solve for Rx using Equations (14-10) by (14-13), the relationship among deflection factor and the meter resistance to the unknown resistance could be display. Given Equation (14-14) is the mathematical representation of this relationship.
Rx =(1 - D/D) Ro (14-14)
If half-scale deflection occurs, then Rx = Ro, so that the value of Ro is marked at mid-scale on the ohm meter face.