Mechanism - charged nucleophiles:
We shall make use of the reaction in to demonstrate the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution. The methoxide ion employs one of its lone pairs of electrons to make a bond to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride. At similar time, the comparatively weak π bond of the carbonyl group breaks and both the π electrons move onto the carbonyl oxygen to provide it a 3rd lone pair of electrons and a negative charge. This is precisely the same 1st step included in nucleophilic addition to aldehydes and ketones.
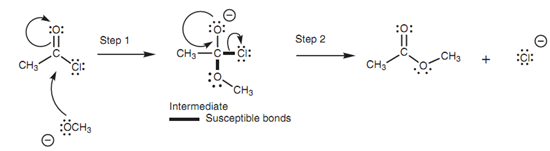
Figure: Mechanism of the nucleophilic substitution.