Addition vs substitution:
Carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives go through nucleophilic substitution whereas aldehydes and ketones go through nucleophilic addition. This is since nucleophilic substitution of a ketone or an aldehyde would produce a carbanion or a hydride ion correspondingly. These ions are not stable and extremely reactive, thus they are only formed with difficulty. Additionally, C-C and C-H σ bonds are not simply broken. Hence, nucleophilic substitutions of aldehydes or ketones are not possible.
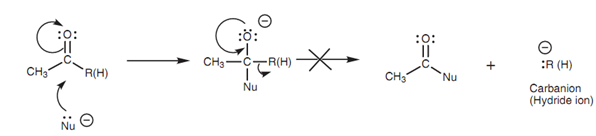
Figure: Unfavorable formation of an unstable carbanion or hydride ion.