Overview:
Generally, addition of charged nucleophiles results in the creation of a charged intermediate. The reaction stops at this stage and acid has to be added to complete the reaction.
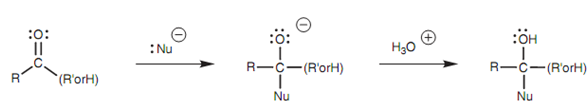
Figure: Nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group.
Neutral nucleophiles in which nitrogen or oxygen is the nucleophilic center are comparatively weak nucleophiles, and an acid catalyst is generally needed. After nucleophilic addition has happened, further reactions may occur leading to structures such like imines, enamines, acetals, and ketals.
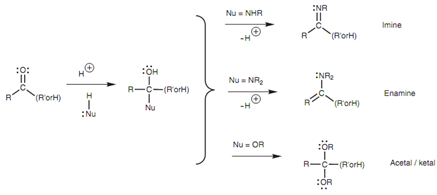
Figure: Synthesis of imines, enamines, acetals, and ketals.