Mechanism of nucleophilic addition:
The 1st stage of the mechanism is a general nucleophilic addition. The amine works as the nucleophile and the nitrogen atom is the nucleophilic center. The nitrogen employs its lone pair of electrons to make a bond to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. Since this bond is being created, the carbonyl π bond breaks with both electrons that moving onto the oxygen to provide it a third lone pair of electrons and a negative charge. The nitrogen as well gains a positive charge, but both these charges can be neutralized through the transfer of a proton from the nitrogen to the oxygen (Step 2).
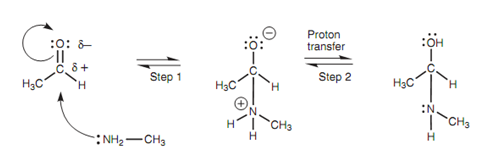
Figure: Mechanism of nucleophilic addition.