Q: Determine the voltage Vo by Norton's theorem, don't utilize node & loop methods. Use super position method.
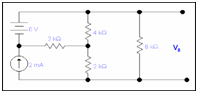
Solution:
We desire to calculate V0 by using Norton's theorem.
Step 1: Replacing RL to a short circuit to search IN.
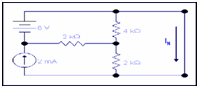
Here RL is equal to 6k resistor.
Step 2:
We can't use node or loop methods, so we have to use super position method to calculate IN
To apply super position technique we will remove all circuits one by one that is after removing voltage source we have to replace it with short circuit and current source with open circuit.
Hint: Don't eliminate all of circuits simultaneously.
When only current source is active
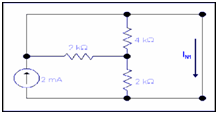
Because of short circuit all current will pass through the short circuit therefore
IN1 = 2mA...................(i)
While only voltage source is active.
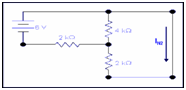
4k is in parallel to 2k resistor which in return in series to 2k resistor .therefore overall resistance.
R = (4k||2k) +2k
= 8/6 k +2k = 3.33 k
Therefore , IN2 = 6/3.33k= 1.80mA -------------- (ii)
Overall IN from both sources so from equation (i) and (ii) we have
IN = IN1 + IN2
= 2mA + 1.80mA //putting value from above
= 3.80mA
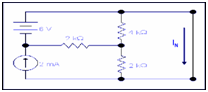
Step 3: determining the value of RN
To calculate value of RN we have to short circuit all voltage sources & open circuit all current sources.
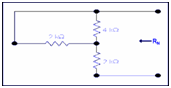
4k is in parallel to 2k.The join effect of these is in series along 2k.
4k||2k + 2k = 1.33 + 2k
=3.33k =RN
Step 4:
After determining IN & RN, re-inserting the load resistance RL in the circuit in parallel RN and letting the IN current source parallel along these two resistances. therefore our Norton equivalent circuit.
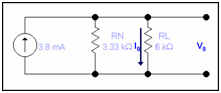
Using current divider rule
I0 = ( 3.80m)(3.33) x 1/9.33k= 1.356 mA
Using ohm's Law
V0 = 6k x 1.35 = 8.143 volts