Wrought Al Alloys
Wrought aluminium alloys are obtained by addition of Mn and Mg. The Al-Mn and Al-Mg alloys cannot be heat treated. Al-Mn alloy combines high ductility with excellent corrosion resistance. Beverage cans, cooking utensils and roofing sheets are made in Al-Mn alloy.
Al alloy that responds to heat treatment by age hardening are Al-Cu, Al-Cu-Mg and Al-Mg-Si. Some Al alloys, their composition and applications are described in Table . Duralumin is one such alloy which contains 4% Cu and small amounts of Mg, Mn and Si. After heat treatment this alloy develops UTS of 450-550 MPa and finds use in aircraft structures.
Apart from cast and wrought alloys the greater tonnage (about 85%) of Al is used in commercially pure form in which impurities are less than 1%. Al extrusions, tube, rods, wire, electrical conductors, chemical process equipment, foils and many architectural fittings are made in commercially pure Al. The properties of aluminium are described in Table .
Table: Some Aluminium Alloys – Properties and Applications
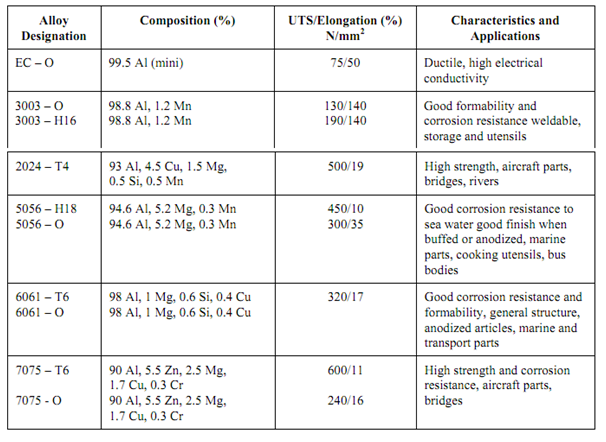
Table: Typical Properties of Aluminium
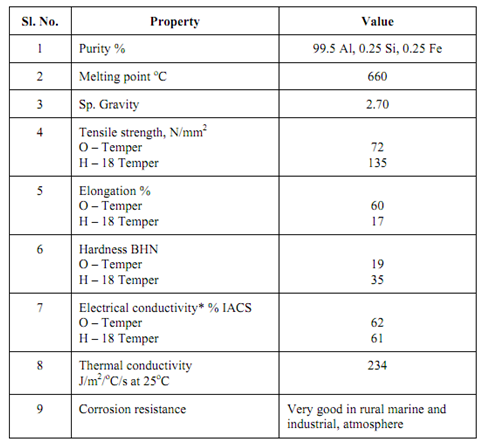
* Compare with copper, 62% of copper electrical conductivity.
In Table aluminium alloys have been assigned certain temper like O-Temper and H- 18 Temper. The temper designation indicates the condition and heat treatment of any given alloy. Generally the temper designation must follow the alloy designation and separated by a dash. For example, the alloys in Table must be described as 3003-O, 2004-T4. The temper designations are described below. There are four basic tempers :
(a) F – As fabricated
(b) O – Annealed
(c) H – Strain hardened
(d) T – Heat treated
H is always followed by two or more digits. The first digit indicates basic operations while the following digit stands for the final degree of strain hardening.
H1 – only strain hardened
H2 – strain hardened and partial annealed
H3 – strain hardened followed by stabilization
The second digit stands for amount for cold work. The digit 8 represents fully cold worked or full hard. The digit of 4 means half hard and 2 means quarter hard. Thus, H18 means full hard by strain hardening only.
T designation is followed by numbers 2 to 9. Their meanings are :
T2 – Annealed (only for castings)
T3 – Solution heat treated and then cold worked
T4 – Solution heat treated and naturally aged to stable condition
T5 – Artificial ageing after any one of the following : Elevated temperature, rapid cool fabrication such as casting or extrusion
T6 – Solution heat treated and fabricated
T7 – Solution heat treated and stabillised
T8 – Solution heat treated, cold worked and then artificially aged
T9 – Solution heat treated, artificially aged and then cold worked.