Amides:
Amides are as well derivatives of carboxylic acids. This time the carboxylic acid is related with an ammonia or amine. Since with esters, the parent carboxylic acid is recognized. This is then known as an alkanamide and involves the nitrogen atom. For instance, linking ethanoic acid along with ammonia provides ethanamide.
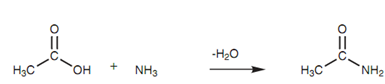
Figure: Formation of ethanamide.
If the carboxylic acid is related with an amine, after that the amide will have alkyl groups on the nitrogen. These are referred as alkyl substituents and come at the starting of the name. The symbol N is employed to depict that the substituents are on the nitrogen and not some another part of the alkanamide skeleton. For instance, the structure in the below figure is termed as N-ethylethanamide.
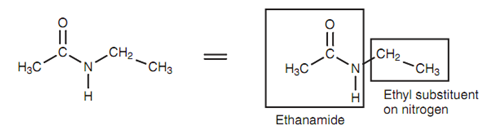
Figure: N-Ethylethanamide.