Nitrogenase complex:
Biological nitrogen fixation is carried out through the nitrogenase complex which consists of two proteins: a reductase, that gives electrons with high reducing power, and a nitrogenase, that uses these electrons to decrease N2 to NH3. The reductase is a 64 kDa dimer of identical subunits which hold one iron-sulfur cluster and two ATP binding sites. The nitrogenase is a bigger protein of 220 kDa which consists of two α- and two β-subunits (α2β2) and contains an iron-molybdenum complex. The transport of electrons from the reductase to the nitrogenase protein is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP through the reductase.
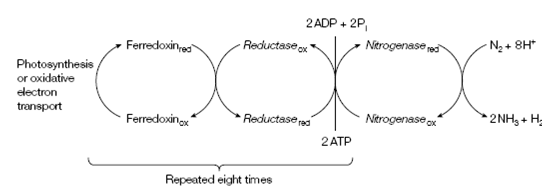
Figure: The flow of electrons in the nitrogenase-catalyzed reduction of N2.
while the reduction of N2 to NH3 is only a six-electron process:
N2 +6 e- + 6H+→ 2NH3
the reductase is imperfect and H2 is also establish. Therefore two additional electrons are also needed:
N2 + 8 e- +8 H+→ 2NH3 +H2
The eight high-potential electrons come from reduced ferredoxin which is produced either in chloroplasts by the action of photosystem I or in oxidative electron transport. The whole reaction of biological nitrogen fixation:
N2 +8 e- +16 ATP +16H2O → 2NH3+H2+16ADP+16Pi+8H+
highlights which it is energetically very expensive, with at least 16 ATP molecules being hydrolyzed.