Definition of learning
Many neural pathways build connections during development which subsequently remain unaltered. These ways are often said to be the generic term and hard wired for those procedure which ensure the pathway is properly connected is specificity. Although, pathways subject to continual re-wiring either during development or as a result of experience are referred to as plastic and the re-wiring processes elaborate as plasticity. Developmental plasticity is wiring which is conditional on early sensory experience and shapes subsequent perception. Learning is the acquisition of reproducible alterations in behavior and is also plasticity as a result of exacting experiences. The storage of the altered behavior over time is memory. In animals, memory and learning can only be tested operationally through recall, in that the previously learned behavior is elicited through the appropriate stimuli.
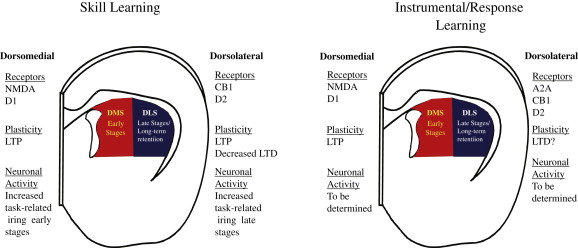
Types of learning
The Learning is acquiring new or modifying skills, existing, behaviors, knowledge, values, or preferences and may include synthesizing various kind of information. The ability to learn is possessed through animals, humans and some machines. The Progress over time tends to follow learning curves. Learning is not necessary it is contextual. It does not happen all at once, but establish upon and is shaped through what we previously know. To that end, learning may be viewed as a procedure, rather than a group of procedural and factual knowledge.Learning is the acquisition of altered behavior as a result of experience and occurs through rewiring of neural pathways (plasticity). Keeping the changes over time is memory. Prior learning is tested through recall, elicited through the appropriate stimuli.