Olfactory receptor neurons
An olfactory receptor neuron (ORN), also known as olfactory sensory neuron (OSN), is a transduction cell inside the olfactory system.Humans have around 40 million olfactory receptors which detect up to 10,000 distinct odors. In vertebrates, the ORNs are bipolar neurons with dendrites facing the interior space of the nasal cavity and an axon which passes via the cribiform plate then travels along the olfactory nerve to the olfactory bulb. The ORNs are situated in the olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity. The cell bodies of the ORNs are circulated amongst all three of the stratified layers of the olfactory epithelium.
A lot of tiny hair-like cilia protrude from the olfactory receptor cells dendrite into the mucus covering the surface of the olfactory epithelium. The surface of such cilia is enclosed with olfactory receptors, a kind of G protein-coupled receptor. Each of the olfactory receptor cell expresses only one kind of olfactory receptor (OR), but many individual olfactory receptor cells express ORs that bind the similar set of odors. The axons of olfactory receptor cells that express the similar OR converge to form glomeruli in the olfactory bulb.
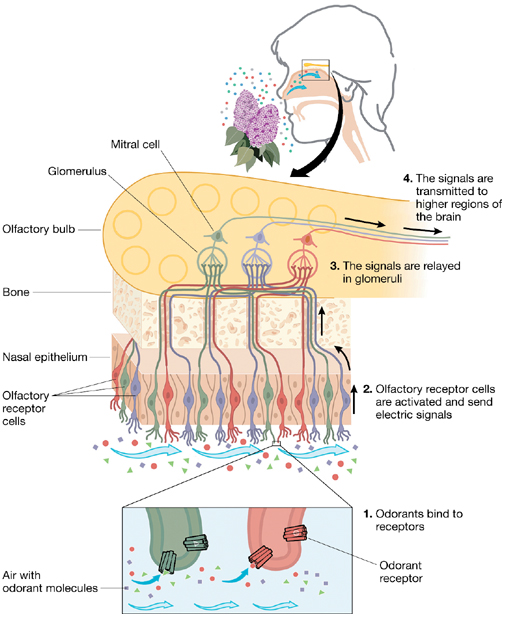
ORs that are located on the membranes of the cilia have been categorized as a complex kind of ligand-gated metabotropic channels. There are around 1000 various genes which code for the ORs, making them the biggest gene family. An odorant will dissolve into the mucus of the olfactory epithelium and then bind to an OR. The ORs can bind to a variety of odor molecules, with changeable affinities. The difference in affinities causes dissimilarities in activation patterns resulting in exclusive odorant profiles. The activated OR in turn activates the intracellular G-protein, GOLF (GNAL), adenylate cyclase and production of cyclic AMP (cAMP) opens ion channels in the cell membrane, resultant in an influx of calcium and sodium ions into the cell, and an efflux of chloride ions. Such influx of positive ions and efflux of negative ions causes the neuron to depolarize, making an action potential.