Neurotransmitter inactivation
After the neurotransmitter molecule has been acknowledged by a post-synaptic receptor, and it is released back into the synaptic cleft. In the synapse, once it should be quickly eliminated or chemically inactivated in order to prevent the constant stimulation of the post-synaptic cell and an excessive firing of action potentials.
A few neurotransmitters are eliminated from the synaptic cleft by special transporter proteins on the pre-synaptic membrane. These transporter proteins bring the neurotransmitter back into the pre-synaptic cell, where it is either repackaged into the vesicle and stored until it is once again required to transmit a chemical message, or broken down by enzymes. The Serotonin is one neurotransmitter which gets recycled in this way. The Serotonin, a small-molecule neurotransmitter found in many regions throughout the brain, is included in a wide variety of behaviors, neuroendocrine function, involving appetite, sleep, memory, sexual behavior, and mood.
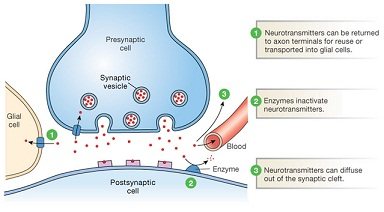
Not all the neurotransmitters are recycled by the presynaptic cell. The Neuropeptide neurotransmitters just rapidly diffuse away from the receptors into the surrounding medium. One main neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, has a particular enzyme for inactivation right in the synaptic cleft known as the acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The AChE is an enzyme present at all cholinergic synapses that serves to inactivate acetylcholine by hydrolysis. The Acetylcholine (ACh), an excitatory small-molecule neurotransmitter found at different locations throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems and at all neuromuscular junctions, is comprised of the acetate and choline. The AChE breaks ACh into its component sections; acetate and choline. After hydrolysis, acetate rapidly diffuses into the surrounding medium, whereas choline gets taken back into the presynaptic cell by a high affinity choline uptake (HACU) system. The Choline is then recycled by the pre-synaptic cell for use in the synthesis of more ACh.