Address Classes
The address class describes in that bits are used for the network ID and that bits are used for the Host ID's. It also describes the possible number of networks and the number of hosts per network the internet community has described three address classes based on the network size.
There are three address classes that are as given below:
Class A Address class
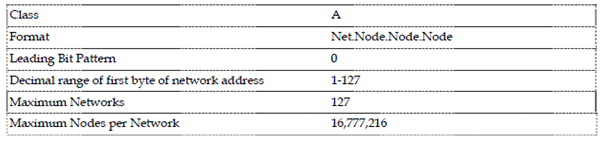
Class A addresses are assigned to networks within an extremely large number of hosts. The high order bit in a class. The network is always set to zero. The next seven bits (finishing the first octet) did the networkID. After that the remaining 24 bits (which from the last three octet) represent the hostID. There could be a maximum of 126 networks and around 17 million hosts per network in a class A address class.
Specification:
Class B Address Class
Class B addresses are assigned to medium-sized to large-sized networks. The two high-order bits in a class B network are always set to binary 10.The next 14 bits done the networkID. After that the remaining 16 bits represent the host ID. There could be a maximum of 16,384 networks and around 65000 hosts per network in class B address class.
Specification:

Class C Address Class
Class C networks are used for small local area networks. The three high-order bits in class C networks are always set to binary 110. The next 21 bits done the networkID. After that the remaining 8 bits represent the hostID. There could be maximum of around 2 million networks and 254 hosts per network in class C address class.
Specification:
