What is NFS?
The NFS was developed to permit machines to mount a disk partition on a remote machine as if it were on a local hard drive. This permits for fast sharing of files across a network. The edition of nfs is 2.
It also provides the potential for unauthorised access of the hard drive over the network (and therefore possibly read the users email and delete files as well as break into the system) NFS is a stateless protocol, that means in which the request that is made between the client and server is done in itself and doesn't need keys of prior transactions.
Network File System services are activated in runlevel 3, nfs is the service that permits the user to share or access the directories, remote files and file systems, nfs service controls four daemons and they are
nfsd
This is the NFS (Network File System) daemon. It runs on the file server and is responsible for handling client requests.
mountd
This daemon runs on the Network File System server and is responsible for responding to client NFS mount requests.
lockd
This is run through both the client and the server, this daemon handles file locks.
statd
This is run through both the client and the server; statd maintains the status of presently enforced file locks.
Rpc.portmapper
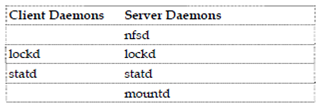
These daemons do not directly give nfs services. These map calls made from other machines to the right nfs daemons. Listing of daemons which are invoked through NFS on both the client and the server hosts are shown as below. It should be noted in which both lockd and statd daemons are invoked on both the hosts.
Table