Nerve cells:
In eukaryotes possibly the most rapid and complex signaling is mediated through nerve impulses. The Nerve cells (neurons) consist of a cell body with numerous projections of the plasma membrane, known as dendrites. These interact with other cells and receive information from them in the form of nerve impulses. Cell body then assimilates the information derived from a number of dendritric contacts and passes on the information as another nerve impulse down the huge axon. The axon ends at the synapse where it makes contact with the post-synaptic (target) cell. The axon is covered in places through a membranous myelin sheath, made up commonly of the lipid sphingomyelin, that acts as an electrical insulator and enabling the nerve impulses to be transmitted over long distances sometimes more than 1 m in larger animals. Each millimeter or so along the axon the myelin sheath is interrupted through
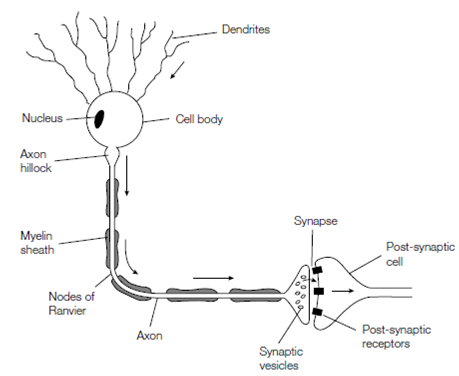
figure: Schematic diagram of a typical nerve cell.
unmyelinated regions known the nodes of Ranvier in the figure. The end of the axon the nerve terminal, is total of synaptic vesicles which store the chemical neurotransmitters, like as acetylcholine. When a nerve impulse reaches the nerve terminal the synaptic vesicles release their contents into the synaptic cleft, the space among the pre- synaptic cells and post-. The neurotransmitter then diffuses across interacts and space with receptors on the surface of the post- synaptic cell which is causing a signal to be transduced in that cell.