Sugar derivatives:
The hydroxyl groups of simple monosaccharides can be replaced with other groups to form a range of sugar derivatives. For instance, phosphorylated sugars like as glucose 6-phosphate are very important metabolites in glycolysis. In amino sugars, one or more hydroxyl groups are every replaced through an amino group (that is frequently acetylated), for instance acetyl -D-N- acetylglucosamine. This and other sugar derivatives are general components of several glycoproteins. Nucleotides, such as ATP, each consist of a sugar in that the anomeric carbon atom has establish a covalent bond with a nitrogenous base. Because the bond is among the anomeric carbon of the sugar and a nitrogen atom of the base, it is known as an N-glycosidic bond. Other modifications involve oxidation of one of the carbons to form a carboxylate sets, so generating a uronic acid. For instance, oxidation of carbon-6 of D-glucose in that way yields D-glucuronic acid. Uronic acids are very important components of several polysaccharides. ketoses and Aldoses can also be reduced to yield polyhydroxy alcohols known as alditols such as sorbitol (D-glucitol), D-mannitol and D-xylitol, that are sweet-tasting and are used to flavor sugarless gum and mints, and glycerol that is an important lipid parts. Alditols are linear molecules which cannot cyclize.
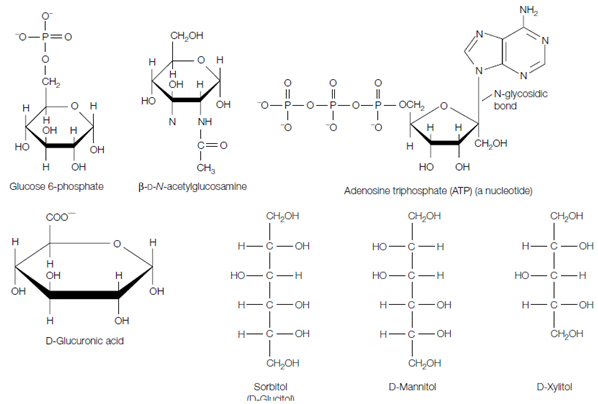
Figure: Examples of sugar derivatives.