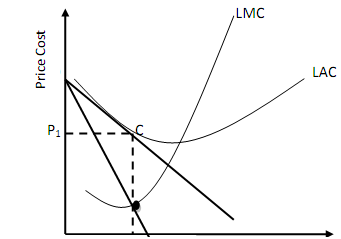
Long-Run Equilibrium Under Monopolistic Competition:
The supernormal profits earned in the short-term is competed away in the long-run as a result of the entry of new firms that are producing close substitutes (as experienced by firms under perfect competition). Eventually, the monopolistically competitive firm will reach long-run equilibrium (profit-maximization) position whereby it receives a price (P) that is equal to long-run average total cost (LAC), so that it will be earning only a normal profit as illustrated in Figure.