Prism Monochromators:
You know in which a prism disperses sunlight into seven various colors. This occurs due to the refraction of the light while it passes by the prism. The radiations of different colors having different wavelengths are refracted to different extent because of the difference in the refractive index of glass for different wavelengths. Shorter wavelengths are refracted more than longer wavelengths as depicted in Figure (a).
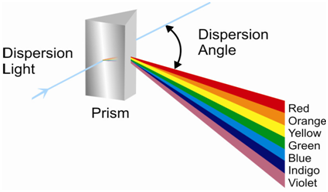
Figure: a) Dispersion of radiation by prism
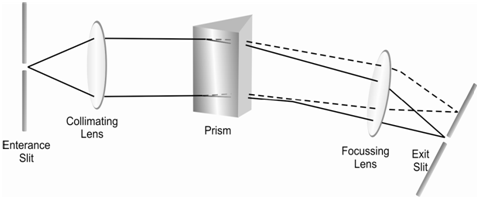
Figure: b) Schematic diagram of the prism monochromator
If a prism is rotated, different wavelengths of the radiation, coming out after refracting by it, could be made to pass by the exit slit. Within a prism monochromator, display in Figure (b), a fine beam of the light from the source is acquired by passing by an entrance slit. This is then collimated on the prism along with the help of a lens. The refracted beams are then focused on an exit slit. The prism is then rotated in a predetermined way to gives the desired wavelength from the exit slit.