Principle of Conservation of Momentum:
It may be observed from impulse momentum equation that when sum of the impulses due to external forces is zero, the momentum of any system remains constant or is conserved. A case of two masses, gun and a shell is a popular instance as a study case. Throughout an extremely small interval of explosion the forces Fs (t ) and Fg (t ) acting on shell and the gun, respectively are equal at all given instant of time and opposite in direction. The sum-total of the impulse (Fs(t ) dt + Fg (t) dt) is thus, always zero. The sum-total of the change in momentum of shell and gun is also zero by virtue of the above referred equation. If ms and mg are masses of shell and gun respectively,
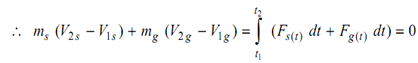 --------- (1)
--------- (1)
ms V2s + mg V2g = ms V1s + mgV1g
where, V1 s and V2 s are the velocities of shell at time t1 and t2, and V1g and V2g are the velocities of gun at time t1 and t2 respectively.
Therefore, Eq. (1) is the statement of the principle of conservation of momentum.