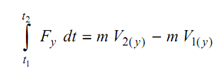Impulse-Momentum Equation:
If Fx is an applied force along with x direction on a body of mass (m) subjected to acceleration x¨ or d / dt ( x? ) , then you shall recall that the Newton's Law of Motion states that,
F x = m x¨ = m d ( x? ) /dt
where, x = distance traversed at any time t,
x? = velocity along x direction at time t, and
x¨ =acceleration along x direction at time t.
Since mass (m) remains constant throughout its motion, we can write :
Fx = d /dt (m x? )
The product (m × x? ) is the momentum of mass (m) by virtue of its velocity (x ) at time (t).
If the applied force Fx varies with respect to time (t) as illustrated in Figure, the impulse
of the force Fx during a short interval (dt) is the product (Fx × dt ) given by the area of the
shaded portion LM M′ L′ illustrated in Figure.
∴ Fx dt = { d/dt (m x? )}dt
Integrating the effect of impulses throughout a period from (t1) to (t2 )
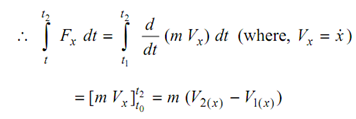
= m (V2( x ) - V1( x ) )
where, V1( x ) is velocity along x direction at time t1, and
V2( x) is velocity along x direction at time t2.
Thus the integrated effect of impulse during time interval from t1 to t2 is the change of momentum of mass m along x direction. This is known as Impulse-Momentum Equation.
Similar equation may be written down in other two directions y and z. If Fy is the component of force along y direction and V1( y ) and V2( y ) are the velocities of the mass along y direction at time t1 to t2 , respectively, then