Reproduction in fungi
Fungal reproduction is complicated reflecting the differences in genetic makeup and lifestyles within this diverse kingdom of organisms. It is estimated in which a third of all fungi reproduce using more than one technique of propagation example for, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle of a species the teleomorph and the anamorph. The Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states which lead to the creation of specialized structures for asexual or sexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction through efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagules.
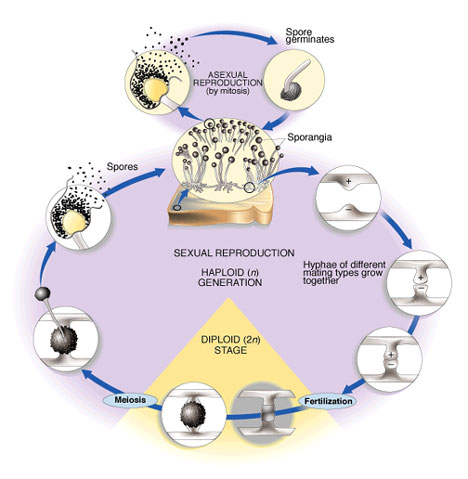
Each of the fungal groups is characterized by differences in their life cycles. All fungi are characterized by having a period of vegetative growth where their biomass rises. The length of time and the amount of biomass needed before sporulation can occur vary. Almost all fungi reproduce by the production of spores but a few have lost all sporing structures and are referred to as mycelia sterilia. Different kinds of spore are produced in different parts of the life cycle.