Fungal structure and growth
Fungi are heterotrophic, eukaryotic organisms with a filamentous, tubular structure, a single branch of which is called a hypha. A network of hyphae is called a mycelium. Hyphae are bound by firm, chitin-containing walls and contain most eukaryotic organelles. Not all fungi are multicellular, some are single-celled and are termed yeasts.
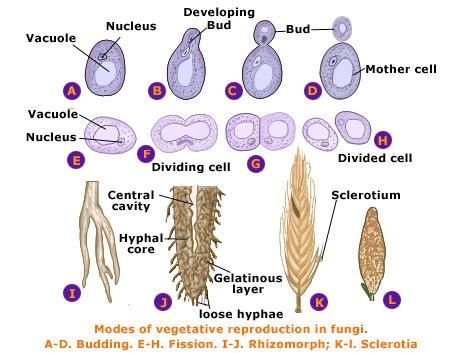
Fungal walls are formed from semi-crystalline chitin microfibrils embedded in an amorphous matrix of b-glucan. In the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota, hyphae grow by tip growth followed by septation. In the Chytridiomycota and Zygomycota fungal hyphae grow by tip growth but remain aseptate.