Enumeration of microorganisms
Many counters are used to estimate the density of microorganisms within a liquid culture. An appropriate dilution or various dilutions within the estimated appropriate range is spread using sterile methods on the agar plate that is then incubated under the appropriate conditions for growth until individual colonies appear. Every colony marks the spot where a single organism was originally placed therefore the number of colonies on the plate equals the number of organisms within the volume of liquid spread on the plate. Which concentration is then extrapolated by the known dilution from the original culture to estimate the concentration of organisms within that original culture?
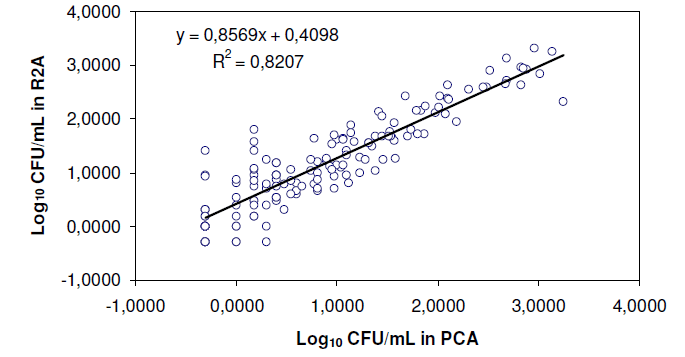
The maximum number of colonies which may be efficiently counted on a single plate is somewhere among 100 and 1,000, depending on the size of the colony and the kind of organism. Enumeration of bacteria is counting the number of viable bacterial cells present in 1g or 1ml of a sample. The bacterial counts are commonly expressed in CFU/ml or CFU/g. CFU-Colony Forming Units.