Cell division and ploidy
Ploidy is the number of groups of chromosomes in a biological cell. Human sex cells have one complete group of chromosomes from the female or male parent. Sex cells, also called gametes combine to produce somatic cells. Somatic cells thus have double as various chromosomes. The haploid number n is the number of chromosomes in a gamete. A somatic cell has doubled which several chromosomes 2n. A Cell division is the procedure through which a parent cell separate into two or more daughter cells. Cell division is commonly a small segment of a larger cell cycle.
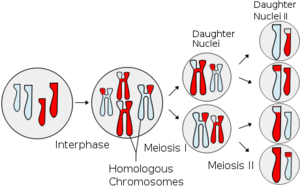
Several organisms have more than two sets of homologous chromosomes and are called polyploid. Humans are diploid. A human somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes: 2 complete haploid sets which make up 23 homologous chromosome pairs.