Cell division
Cell division is the procedure through that a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division is commonly a small segment of a bigger cell cycle. This kind of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again and again. The corresponding sort of cell division in prokaryotes is identifying as binary fission. In another category of cell division present only in eukaryotes called meiosis a cell is permanently transformed into a gamete and may not divide again until fertilization. Just before that the parent cell splits it undergoes DNA replication.
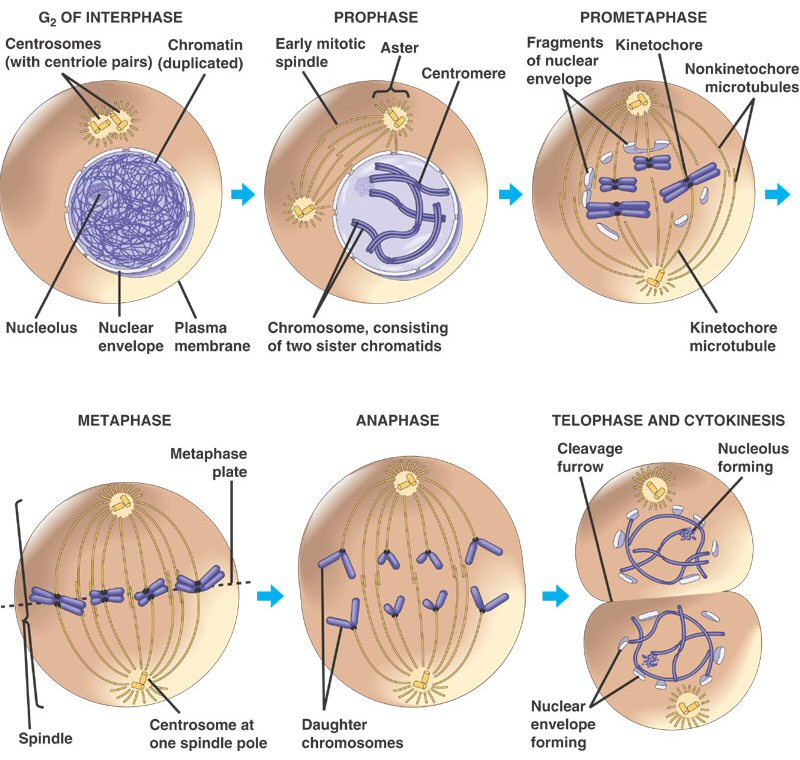
The primary concern of cell division is the maintenance of the original cell's genome. Before division can occurrence the genomic information which is stored in chromosomes must be replicated and the duplicated genome must be divided cleanly among cells. The great deal of cellular infrastructure is involved in keeping genomic information consistent among generations.