Metal Melting:
The fundamental melting process operations are following:
- Furnace charging, in which, scrap, metal, carbon, alloys and flux are added to the furnace,
- melting, through which the furnace remains closed,
- Back charging, that involves the addition of more metal and alloys, as required,
- refining and treating, throughout which the chemical composition is adjusted to meet product qualifications
- slag eliminating (another step in the metal melting procedure) involves eliminating the slag in the furnace from a tapping hole or door. As slag is lighter than molten iron, this remains atop the molten iron and may be raked or poured out of cupola furnaces from the slag hole situated above the level of the molten iron. Electric arc & induction furnaces are tilted backwards, and their slag is eliminated through a slag door, and
- tapping molten metal into a ladle or directly into moulds.
Foundries melt metals is one of various types of furnaces based on the kind of metal being utilized (Table 1). Furnaces types include electric arc, cupolas, induction, or reverberatory etc. Due to the different nature of metals, different kind of inputs is needed.
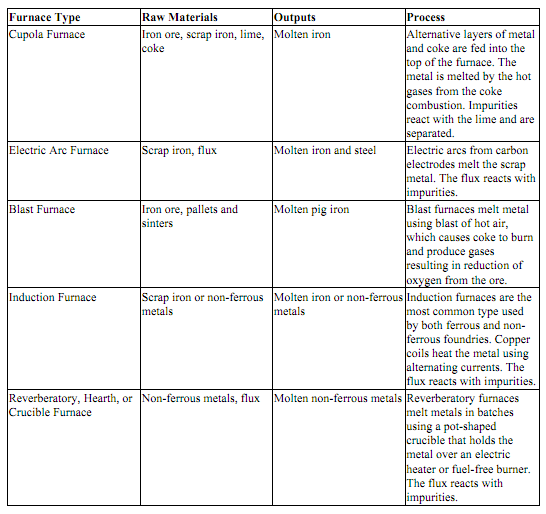
Table : Common kinds of Metal Melting Furnaces
In the next sections of this unit, above indicated different furnaces are described in detail. There are various other types of furnaces available however it is not possible to discuss each kind in this unit. Just the commonly utilized types have been briefed in the next few sections.