Electrodialysis:
Electrolysis is a membrane process wherein preferential transport of cations and anions are achieved using cation and anion selective membranes as a result of an electrical driving force. Using this procedure, the concentration of ionic species can be increased or decreased so that practical concentration or depletion of electrolyte solutions is possible. Along with ion selective membranes of precent origin which are more permeable to univalent cations or anions, electrodialysis process can be used to simultaneously separate and concentrate univalent ions from solutions containing mixtures of uni and multivalent electrolytes. The principle of this process has been already explained. Commonly, the feed electrolyte solution while cations and anions are erased is termed dialysate and the receiving solutions while the ions are added are termed as brine. During electrodialysis process, a number of transport processes occur simultaneously which are illustrated in Figure.
AE,CE= Anion selective, cation selective membranes, C,A,CA = cation, anion, electrolyte
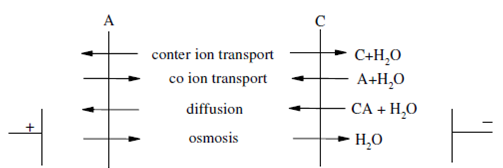
Figure: Various transport processes occurring in electrodialysis process
The counter ion (that having opposite charge compared to that of the fixed group of the membrane) transport constitutes the main electrical ion movement within the process. Anion is the counter ion for anion choosen membranes and cations are the counter ions for cation selective membranes.The counter ion permeation by the membranes carries along with them a certain quantity of water through electro osmosis.