Membrane protein purification and reconstitution
The first step of the purification of an integral membrane protein is to disrupt its interactions with other integral proteins and the lipids in the membrane. This is generally achieved through adding a detergent that solubilizes the membrane. In the order to solubilize membrane but not denature the protein gentle detergents like as octyl glucoside or Triton X-100 is used rather than the harsh detergent SDS. they readily intercalate into the lipid disrupt and bilayer the hydrophobic interactions as the detergent molecules are themselves amphipathic .
At Once solubilized, the hydrophobic region of the integral protein is coated with a layer of detergent molecules that enables the protein to remain in solution. The solubilized protein can then be purified as for a water-soluble
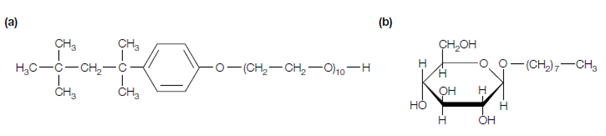
Figure: Structures of (a) Triton X-100 and (b) octyl glucoside.
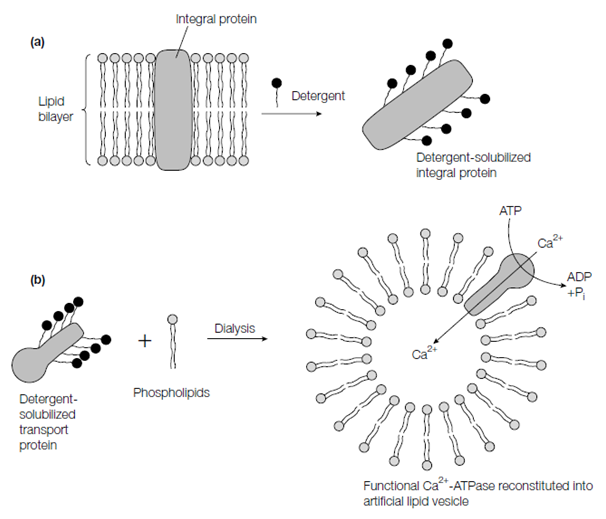
Figure: (a) Detergent solubilization and (b) reconstitution into artificial lipid vesicles of an integral membrane protein.
globular protein as long as detergent is reserved in the buffers to avoid aggregation and loss of the protein. Once the purified, an integral protein can be reincorporated into artificial lipid vesicles liposomes in order to learning its function in above figure. If the phospholipids are added to the protein in detergent solution and detergent dialyzed away the phospholipid vesicles holding the protein will spontaneously form. The method of the protein can then be studied. For instance, if the Ca2+ -ATPase is reincorporated into lipid vesicles then its function example transport of Ca2+ upon ATP hydrolysis can be studied via monitoring ATP to the outside and Ca2+ on the inside of the vesicle upon addition of Ca2+.