Mechanism for the reaction of a hydroxide ion:
In this instance, a lone pair of electrons from oxygen is employed to form a bond to the proton. Through doing so, the oxygen efficiently 'loses' one electron and the proton efficiently gains one electron. The result of it is that, the oxygen loses its negative charge and the proton loses its positive charge.
Curly arrows describing what occurs to all the valence electrons throughout a reaction mechanism can be rather long-winded if you are trying to describe it all in words. Fortunately, there is a diagrammatic manner of displaying the same thing - by using curly arrows. For instance, the mechanism explained above can be explained via using a curly arrow to show what occurs to the lone pair of electrons shown in the below figure. In this case, the arrow begins from a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen (the source of the two electrons) and points to the center of the new bond will be created.
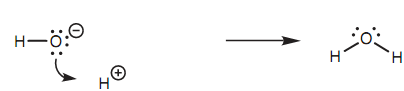
Figure: Mechanism for the reaction of a hydroxide ion with a proton.