Thermodynamic Systems and Processes
Defining a suitable system can significantly simplify a thermodynamic study. A thermodynamic system is any 3-dimensional area of space which is surrounded by one or more surfaces. The surrounding surfaces might be real or imaginary and might be at rest or in action. The boundary might change its size or shape. The area of physical space which lies exterior the chosen boundaries of the system are termed as the surroundings or the atmosphere.
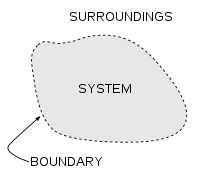
The thermodynamic system is an accurately specified macroscopic area of the universe, defined by boundaries or walls of specific natures, altogether with the physical surroundings of that area, that determine procedures which are permitted to affect the internal of the area, studied by using the principle of thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics includes the study of different systems. A system in thermodynamics is not anything more than the collection of matter which is being studied. A system could be the water inside one side of a heat exchanger, the fluid within a length of pipe, or the whole lubricating oil system for a diesel engine. Establishing the boundary to resolve a thermodynamic problem for a system will based on what information is known regarding the system and what question is inquired regarding the system.
The system undergoes a thermodynamic procedure whenever there is some kind of energetic change inside the system, usually related with changes in volume, pressure, internal energy, temperature, or any kind of heat transfer.
There are numerous particular kinds of thermodynamic procedures which happen often sufficient (and in practical conditions) that they are usually treated in the study of thermodynamics. Each has a exclusive trait which identifies it, and which is helpful in examining the energy and work changes associated to the procedure.
(A) Adiabatic process - a method with no heat transmit into or out of the system.
(B) Isochoric process - a method with no alter in volume, in which situation the system does not work.
(C) Isobaric process - a method with no alter in pressure.
(D) Isothermal process - a method with no alter in temperature.