Temperature And Zeroth Law Of Thermodynamics
The temperature is one of the main quantities considered in the field of thermodynamics. Thermodynamics examines the relation among heat and work, by using an extraordinary scale of temperature termed as the absolute temperature, and therefore associates temperature to work. In thermodynamic terms, the temperature is a macroscopic intensive variable since it is independent of the bulk quantity of elementary entities contained within, be the atoms, molecules, or electrons. The real world systems are frequently not in thermodynamic equilibrium and not homogeneous. For study by techniques of classical irreversible thermodynamics, a body is generally spatially and temporally separated conceptually into imagined 'cells' of small size. When classical thermodynamic equilibrium situations for matter are fulfilled to good estimation in each 'cell', then it is homogeneous and a temperature exists for it, and local thermodynamic equilibrium is thought to prevail during the body.
The Zeroth law of thermodynamics is a generalization theory of thermal equilibrium amongst bodies, or thermodynamic systems, in contact. The Zeroth law defines that when two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
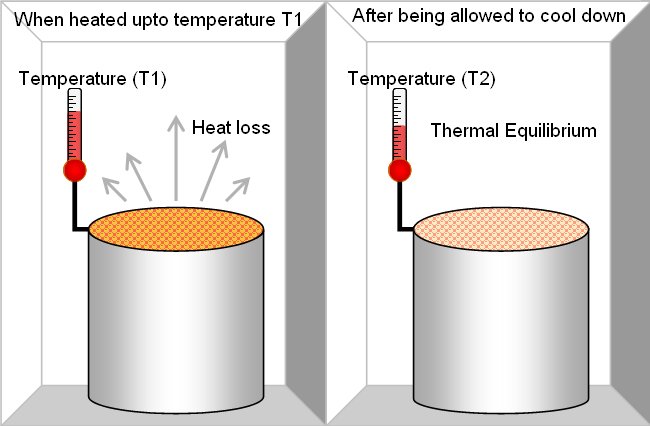
The systems are thought to be in thermal equilibrium when they are able to transfer heat among each other (for illustration by conduction or radiation) though doing not do so. Systems can also be thought to be in thermal equilibrium when they are not capable to transfer heat to each other, though would not do so if capable. The law implies that thermal equilibrium among systems is a transitive relation that affords the definition of an empirical physical parameter, termed as temperature. The temperatures are equivalent for all systems in thermal equilibrium. The law allows the construction of a thermometer to measure such property.