Reciprocating Compressors
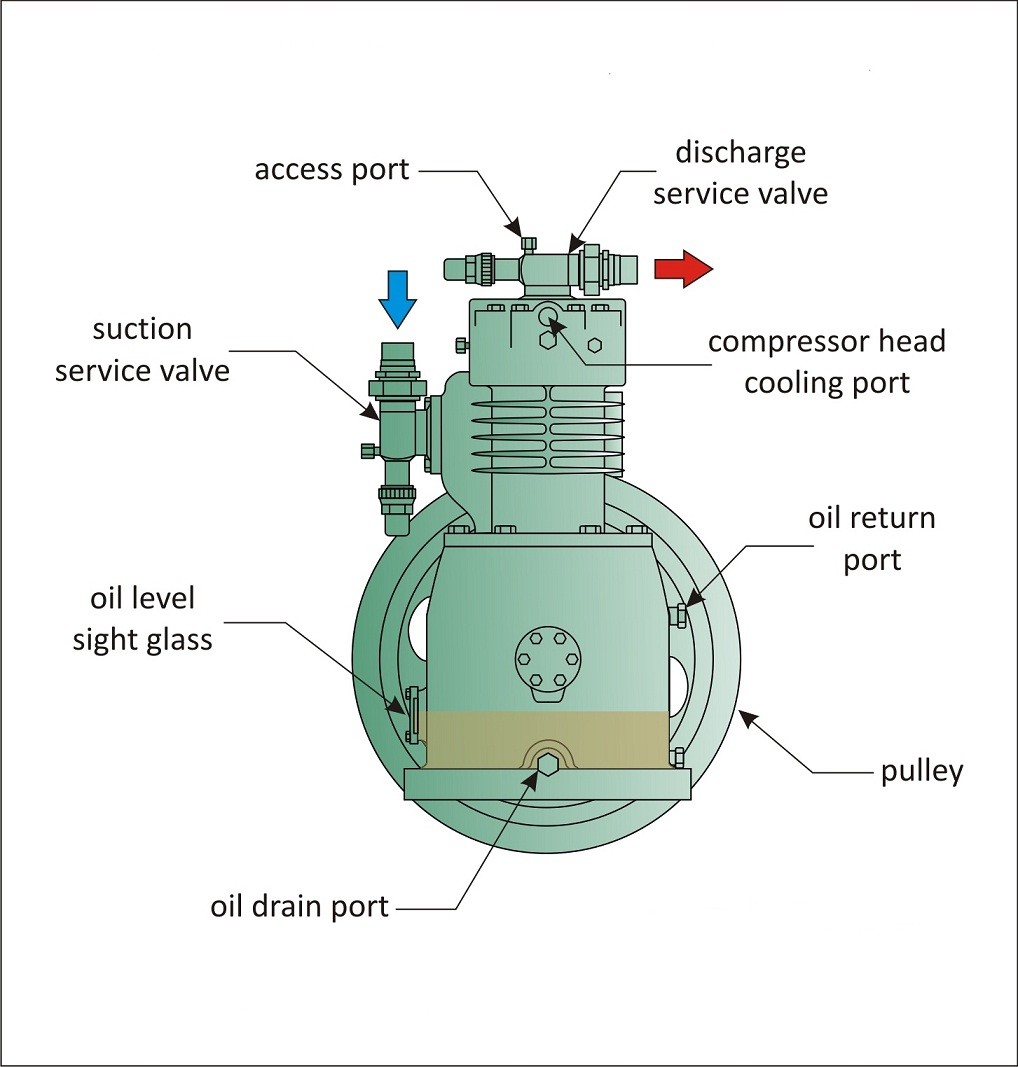
The reciprocating or piston compressor is a positive-displacement compressor which uses pistons driven by a crankshaft to distribute gases at high pressure.
The intake gas comes into the suction manifold, then flows in compression cylinder where it acquires compressed by a piston driven in a reciprocating motion through a crankshaft, and is then discharged. Applications involve gas pipelines, oil refineries, chemical plants, natural gas dealing out plants and refrigeration plants. One specialty application is the blow of plastic bottles made up of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
In a reciprocating compressor, the volume of gas is drawn into a cylinder; it is bounded, and compressed by piston and then discharged into discharge line. The cylinder valves organize the flow of gas via the cylinder; such valves act as the check valves. There are two kinds of reciprocating compressor
(i) Single – Acting compressor:
It is a compressor which has one discharge per revolution of crankshaft.
(ii) Double – Acting Compressor:
It is a compressor which completes two discharge strokes per revolutions of crankshaft. Most of the heavy-duty compressors are double acting.