Energy, Work and Heat
In this section, we establish energy, work, and heat. Energy and associated quantities explain the capacity of a system to execute work. Energy is conserved, that means that it flows, therefore this capacity to execute work can be moved from one place to other. We introduce two essentially significant ideas: the First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics. The First Law explains the conservation of energy and the interchangeability of heat and various kinds of work. The Second Law explains the tendencies of systems to symmetry.
Energy generally has units of joules (J), watt-hours (W h), calories (cal), or BTUs (British Thermal Units). The rate of energy transfer per unit time from one form to other is termed as power, and is usually measured in watts (W) or J s-1.
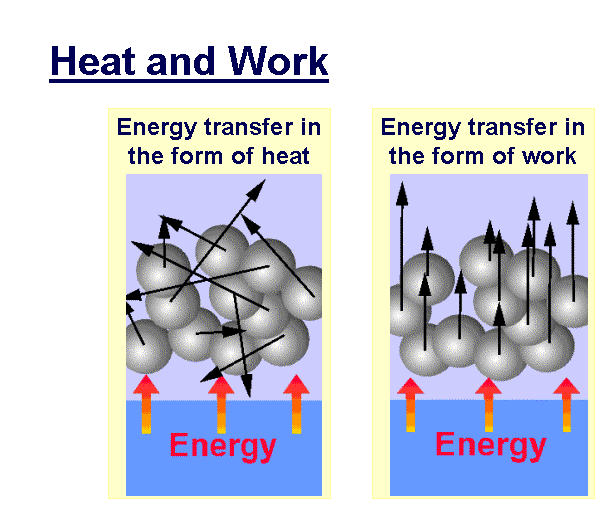
Heat and work are the two manners in which energy can be transferred across the border of a system. One of the most significant inventions in thermodynamics was that the work could be transformed into an equivalent quantity of heat and that heat could be transformed into work.
Whenever a system experiences a change, the change is attended by a change in the energy content of the system. It is the aim of thermodynamics to be capable to explain the change in energy content, and to associate it to the performance of work and the transfer of heat amongst the system and the surroundings. For any change in the system, we can define an initial state and a final state, and we must look for parameters that define the energy content of the system in terms of values that are a exclusive function of the state of the system. These parameters are termed as variables of state. For illustration, the operation of an "ideal gas" engine can be explained in terms of a cycle of states, each of which has an exclusive set of values for P, V, T, and therefore energy content, E.
Since the values for variables of state are an exclusive function of the state, they are self-governing of the pathway by which a change in state happened. Accordingly, variables of state have the property which the sum of changes in value, on going through a sequence of changes of state that form a cycle, is zero. This is obviously the situation, because in a cycle, the first and final states are similar.