Compression Processes
Compression processes are very general in many kinds of industrial plants. Such processes differ from being the main function of a piece of tool, like air compressor, to an incidental outcome of other process, like filling a tank with water without primary opening the valve.
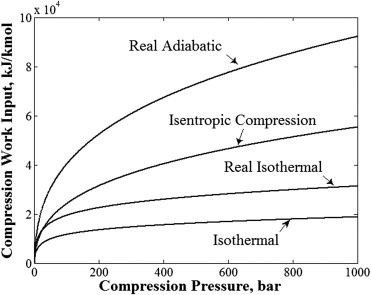
The association among pressure and density whenever compressing gases based on the nature of the process shown below.
(A) Isothermal Compression Processes:
When a compression occurs under constant temperature cases - the process is said to be isothermal. The isothermal process with Ideal Gas Law can be stated as:
pV = constant or
p1V1 = p2V2
(B) Isentropic (or adiabatic) Compression Processes:
When a compression of a gas occurs with no flow of heat energy either into or out of the gas then the process is said to be isentropic or adiabatic. The isentropic process can be stated with the Ideal Gas Law as
pVk= constant or
p1V1k = p2V2k
(C) Polytropic Compression Process:
The isothermal process should occur very gradually to maintain the temperature in the gas constant. The adiabatic process should take place very quickly without any flow of energy in or out of the system. In practice most of the expansion and compression processes are anywhere in among, or said to be polytropic.
pVn= constant or
p1V1n = p2V2n