Reciprocating Compressors:
The reciprocating air compressor, described in below Figure that is the most general design employed today.
The reciprocating compressor generally consists of the subsequent components.
a. The compressing element, heads and pistons, consisting of air cylinders, and air inlet and discharge valves.
b. A system of connecting rods, crossheads, piston rods, and a crankshaft and flywheel for transmitting the power established through the driving unit to the air cylinder piston.
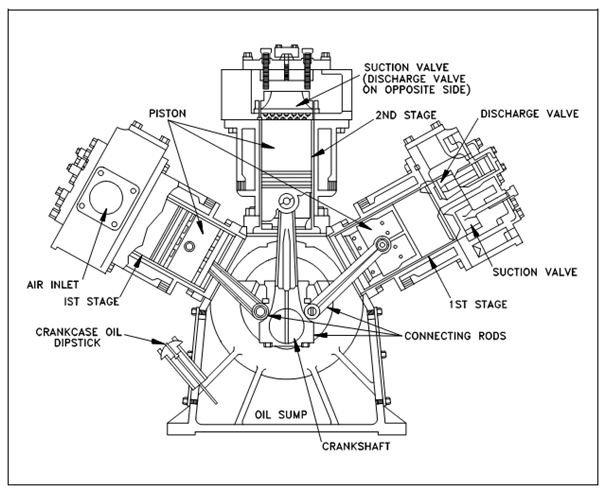
Figure: Reciprocating Air Compressor
c. A self-contained lubricating system for gears, bearings, and cylinder walls, involving a reservoir or sump for the lubricating oil, and a pump, or other denote of delivering oil to the several categories. On a few compressors a separate force-fed lubricator is installed to supply oil to the compressor cylinders.
d. A regulation or control system designed to manage the pressure within the discharge line and air receiver (storage tank) inside a predetermined range of pressure.
e. An unloading system that operates in conjunction along with the regulator, to decrease or eliminate the load put on the prime mover while beginning the unit.