Centrifugal Compressors
The centrifugal compressor, originally built to handle just large volumes of low pressure gas and air (maximum of 40 psig), that has been establish to enable it to move large volumes of gas along with discharge pressures up to 3,500 psig. Therefore, centrifugal compressors are now most often used for medium volume and medium pressure air delivery. One benefits of a centrifugal pump is the smooth discharge of the compressed air. The centrifugal force utilized through the centrifugal compressor is the similar force utilized through the centrifugal pump. An air particle enters the eye of the impeller, designated D within Figure. As the impeller rotates then air is thrown against the casing of the compressor. The air becomes compressed as more and more air is thrown out to the casing through the impeller blades.
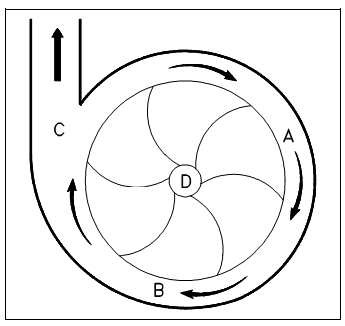
Figure: Simplified Centrifugal Pump
The air is pushed along the path designated A, B, and C in Figure 6. A pressure of the air is raised as it is pushed along this path. Remember in Figure in which the impeller blades curve forward, that is opposite to the backward curve used in classical centrifugal liquid pumps.
Centrifugal compressors could use a variety of blade orientation involving both forward and backward curves as well as other designs.
There might be various stages to a centrifugal air compressor, as within the centrifugal pump, and the output would be the similar; a higher pressure would be generates. The air compressor is used to make compressed or high pressure air for a variety of uses. A few of its uses are pneumatic sensors, pneumatic control devices, pneumatic motors, pneumatic valve operators, and starting air for diesel engines.