Bill of Material (BOM):
A bill of material is a list of the materials along their quantity required to produce one unit of a product, or end item. Hence, each manufacturing product has a bill of material. A bills of material file some time termed as product structure file. BOM is a complete list of all finished products, the quantity of each material in each of the products and the structure of assemblies, subassemblies, parts, and raw materials and their relationship with the products. Another term for a bill of material is indented bill of material. It a list in which the parent is in the margin and its components are indented to show structure.
Generally the bil1s of material file is up-to-date computerized files that must be revised as products are redesigned. The main hurdle associated with BOM is its accuracy that must be overcome in most MRP applications. With the confidence that the file is correct, once the MRS is prepared, end item in the MPS can be exploded into the assemblies, subassemblies, parts and raw materials required. These units can be either purchased from outside suppliers or produced in in-house production departments.
In fact BOM identifies the component parts of final output product. At each level different component, material or sub-assemblies are shown, so the bill of requirements shows not only the total number of sub-parts but also the manner in which these parts eventually come together to constitute the final product. The lead time among the levels is also shown as illustrated in Figure. Each of the items is assigned to only one level, and each item at each level has a unique coding. The different level can correspond to different design. Where complex end products may be made in many different possible configurations from a large number of parts or sub-assemblies which can be assembled in distinct ways, it is common to use a modular bill of requirement structure.
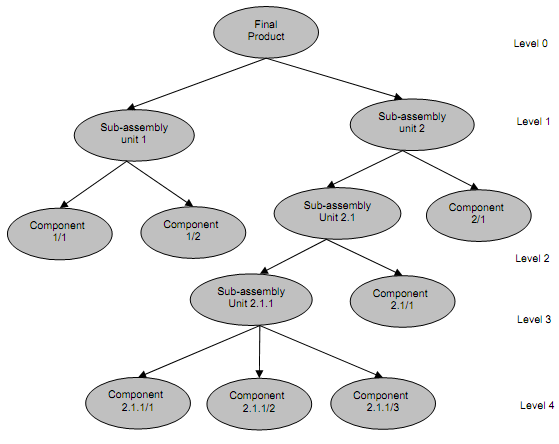
Figure: Basic Structure of Bill of Material