Equilibrium of the Firm:
The equilibrium of the firm graphically represented in figure, by super-imposing Figure in a single g - d plane,
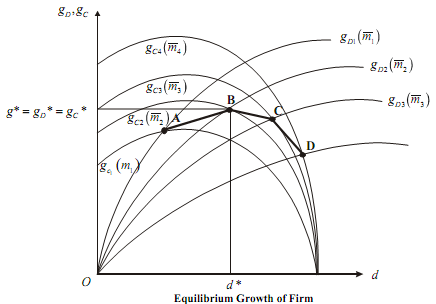
Joining the points of intersection of gD and gC curves, we obtain the ABCD curve, which is shown as the bolder curve. This curve is what Marris calls the balanced growth curve (BGC) given the financial coefficient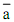 .
.
The firm is in equilibrium when it reaches the highest point on the BGC, which is point B in Figure, given that firm has decided on its financial policy denoted by 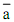 . The balanced growth rate g* is compatible with a unique pair of values of the policy variables m* and d*. Thus, we get,
. The balanced growth rate g* is compatible with a unique pair of values of the policy variables m* and d*. Thus, we get,
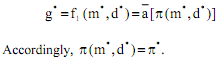
Thus, we see that profit gets endogenously determined in the Marris model.