Old Age of Wear out Failures
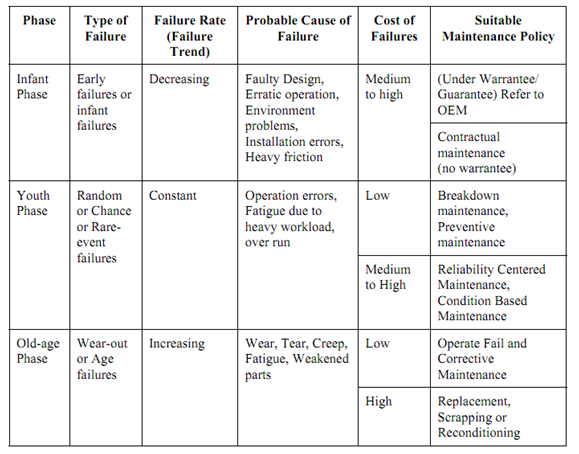
Most of the efforts put by maintenance are attributed to this stage and costs could go high at this stage if this stage is not detected. Calendar time is not only the scale for detection of this stage. For instance a machine used sparingly and a machine used continuously will not reach to the old age stage at the same time, though they are bought at the same time. Hence one should notice that the operational period, conditions maintained while usage, care and efforts put on it to increase its life during its infant and young stages, etc. are a few factors governing the old age failures, where these failures are mainly because of the worn out parts of the machines. As and when this stage is noticed in the machine, a plant engineer may have to choose one of the following alternative strategies.
- Replacement of the machine with a new one.
- Reconditioning of the machine.
- Updating with the new technological features.
- Operate to failure and corrective maintenance (as long as its average annual maintenance cost is less than or equal to the interest on the cost of the new machine) or selling in second sale.
- Scrapping
It is important to note here that the age of a machine (Infant/Young/Middle/Old) is not just decided by the calendar time but by its running time and other factors such as environment, usage, etc.
Table: Failure Analysis through Machine Behaviour and Machine Life Cycle